Types of Micropiles: Your Guide to Foundation Reinforcement
When it comes to foundation reinforcement, micropiles offer a versatile and reliable solution, especially in areas with challenging soil conditions or limited access. Whether you’re dealing with a new construction project or reinforcing an existing foundation, understanding the different types of micropiles can help you make informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll explore the various types of micropiles, their benefits, and when to use them, providing you with a comprehensive overview to ensure your foundation remains strong and stable for years to come.
Read on to learn more about the different types of micropiles and their benefits.
For a Free Expert Opinion and Tailored Quote in Long Island, Brooklyn, or Queens, NY, Contact Piers and Piles Today!

What Are Micropiles?
A micropile is a small-diameter, high-capacity foundation support element used to support structures in challenging soil conditions. Typically less than 12 inches in diameter, micropiles are drilled and grouted piles reinforced with steel, designed to transfer loads to more stable soil or bedrock below the earth’s surface. Their adaptability makes them ideal for confined spaces, retrofits, and projects where traditional piling methods are not feasible.
Learn more about micropiles here.
Benefits of Micropiles:
Micropiles offer several benefits that make them an ideal choice for foundation support in both residential and commercial projects. From their adaptability to various soil conditions to their ability to be installed in tight spaces, micropiles provide a reliable and efficient solution for challenging foundation needs.
Here are some of the key advantages of micropiles that set them apart:
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Minimal Disturbance
- Versatility
- High Load Capacity
- Adaptability to Restricted Access
What Are Micropiles Used For?
Micropiles are commonly used for foundation repair, seismic retrofitting, and stabilizing structures in areas with limited access or difficult soil conditions. Their versatility makes them an ideal solution for a variety of residential and commercial projects.
Key applications of micropiles:
- Foundation Repair: Reinforce existing foundations suffering from settlement or instability, offering effective stabilization with minimal excavation.
- Seismic Retrofitting: Transfer loads to more stable soil or bedrock in earthquake-prone areas, reducing the risk of structural damage.
- Confined or Challenging Spaces: Ideal for use in tight spaces or unpredictable soil conditions, commonly found in urban environments or difficult terrains.
- Infrastructure Projects: Used in large-scale projects like bridges, retaining walls, and towers, where high load-bearing capacity and versatility are required.
- Underpinning: Strengthen and stabilize structures with compromised foundations, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
- New Construction Support: Provide reliable foundation support in areas with weak soil or limited access, allowing for more complex builds.
Micropiles’ adaptability to different soil types and project demands makes them a preferred choice for both residential and commercial applications.
Most Common Types of Micropiles for Foundation Support
Choosing the right type of micropile is critical to ensuring strong and reliable foundation support, especially in New York’s varied and challenging soil conditions. Each type is categorized based on the construction process, which directly influences their performance and suitability for various projects. Whether it’s the simplicity of Type-A cement slurry gravity filling or the enhanced consolidation provided by Type-D repeat grouting, choosing the right micropile type ensures that your foundation is stable, secure, and tailored to the specific demands of your project.
- Drilled Micropiles: Drilled micropiles are small-diameter, reinforced piles with precision installation; ideal for confined spaces and variable soil conditions requiring load transfer.
- Battered Micropiles: Angled micropiles offering enhanced stability and load distribution; best for resisting lateral loads in unstable soil conditions.
- Crux Micropiles: Specialized micropiles providing support in complex foundation challenges; suitable for projects requiring high adaptability in difficult soils.
- Hollow Bar Micropiles: Hollow bar micropiles are threaded hollow steel bars for simultaneous drilling and grouting; excellent for immediate load transfer in loose soils.
- Driven Micropiles: Steel shafts driven into the ground, then grouted; cost-effective, quick installation for deep foundation support in various soils.
- Grouted Micropiles: High-strength grout surrounds steel reinforcement; provides stability through friction and end-bearing in complex soil conditions.
- Helical Micropiles: Steel shafts with helical plates screwed into the ground; fast installation, ideal for tight spaces and challenging soils.
- Helical Pulldown Micropiles: Combines steel and grout for durable support; best for varied soil types needing high load capacity and stability.
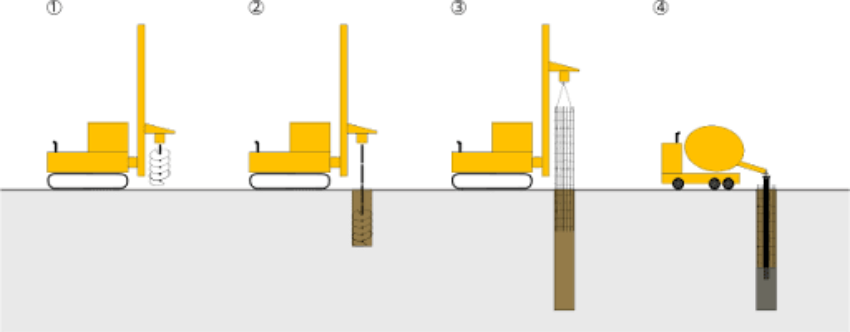
Micropile Installation Procedure: Step-by-Step
The micropile installation procedure involves a series of precise steps, from drilling and grouting to load testing and final verification. Proper execution of each step is essential for ensuring the stability and performance of the installed micropiles.
Micropile Installation Procedure:
- Planning and Design: The process begins with a detailed design that considers soil conditions, load requirements, and project constraints. Engineers determine the ideal placement, depth, and diameter for each micropile.
- Site Preparation: Before drilling begins, the site is cleared, and drilling equipment is set up. Careful attention is given to access points and potential obstacles that could affect the installation.
- Drilling: A small-diameter hole is drilled into the soil to the required depth, reaching either stable soil layers or bedrock. Depending on the soil type, casing may be used to prevent collapse during drilling.
- Reinforcement Insertion: Once the hole is drilled, steel reinforcement (solid or hollow bar) is inserted into the borehole. The type of reinforcement depends on the specific project requirements.
- Grouting: Grout is injected under pressure into the borehole, filling voids and bonding the reinforcement to the surrounding soil. Grouting can be done in stages or continuously, depending on the method chosen.
- Load Testing: After the grout sets, load testing is performed to verify that the micropile meets the necessary load capacity. Adjustments can be made if the test results do not meet specifications.
- Final Verification and Cleanup: Once all micropiles are installed and tested, the site is cleaned up, and the foundation is ready for the next phase of construction.
This step-by-step micropile installation procedure ensures that the foundation remains stable and capable of supporting the intended loads, even in challenging soil conditions.
Note to Builders and DIYers: Understanding Micropile Sizes and Casing
When it comes to micropile and casing sizes, it’s essential to understand how these dimensions impact your project. The right micropile size ensures optimal load-bearing capacity, while casing provides crucial protection from environmental factors like soil corrosion. Whether you’re working on a large infrastructure project or a smaller residential foundation repair, choosing the appropriate sizes can significantly affect both installation and long-term performance.
About Micropile Sizes
- Micropile Sizes: Micropile sizes encompass the overall diameter and length of the micropile, including the steel reinforcement and grout. The diameter can range from 3 to 12 inches, with lengths varying based on the depth required to reach stable soil or bedrock. The size is chosen based on the specific load-bearing needs and the subsurface conditions, ensuring optimal support for the structure.
Micropile Casing Sizes
- Micropile Casing Sizes: Micropile casing sizes refer to the diameter and thickness of the steel casing used in the construction of micropiles. The casing is critical for providing structural support and protecting the micropile from soil and environmental factors. Common casing sizes typically range from 3 to 12 inches in diameter, depending on the load requirements and soil conditions. Thicker casings are used for higher load-bearing applications or in environments with aggressive soil conditions that may cause corrosion.
What to Look for in a Micropile Installation Contractor?
Choosing the right foundation support contractor is crucial for ensuring the long-term stability of your property. The complexity of foundation repair and reinforcement projects requires a contractor with the right expertise, equipment, and attention to detail.
Here are key factors to consider when selecting a foundation support contractor:
- Experience and Specialization: Look for contractors who specialize in foundation support and have extensive experience with the specific types of micropiles your project requires. A knowledgeable contractor will be familiar with the latest techniques and best practices for installing micropiles, helical piers, and other support systems.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure that the contractor is fully licensed, insured, and certified to perform foundation work in your area. They should also adhere to local building codes and industry standards, providing peace of mind that your project is in capable hands.
- Reputation and Reviews: Check for positive customer reviews and testimonials from previous clients. A contractor with a strong track record of successful projects is more likely to deliver quality results.
- Customized Solutions: Every foundation project is unique, so your contractor should offer tailored solutions based on a thorough site assessment. Look for companies that take the time to understand your property’s specific needs and design a plan that addresses those requirements.
- Transparent Communication and Pricing: A reliable contractor should provide clear communication and a detailed estimate that outlines all costs. They should also be upfront about potential challenges and maintain transparency throughout the project.
Types of Micropiles: Final Thoughts
Micropiles are the smart choice for foundation reinforcement in New York’s challenging urban landscapes. At Piers and Piles, we specialize in installing the types of micropiles that offer superior stability, even in diverse soil conditions. Whether you’re dealing with tight urban sites in Brooklyn or flood-prone areas in Long Island, our expertise ensures your foundation is secure and long-lasting. Trust Piers and Piles to provide the right types of micropiles for your project. Contact us today for a free expert assessment and protect your investment.
If You’re from the Long Island, Brooklyn, or Queens, NY, Areas, Click the Button Below to Schedule Your Free Expert Assessment! Let Piers and Piles Provide the Peace of Mind You Deserve—Secure Your Foundation’s Future with the Trusted Experts Today!