In this stage, engineers meet with project stakeholders to discuss site-specific challenges, project goals, and necessary testing requirements. The team evaluates the project scope, existing site conditions, and regulatory guidelines to develop a comprehensive soil testing plan. This preparation ensures the testing aligns with project objectives and sets the foundation for accurate data collection.
Geotechnical Engineering Soil Testing Explained
Geotechnical engineering soil testing is important for understanding subsurface conditions and ensuring stable foundations. This critical process examines soil properties to determine their suitability for construction projects, ensuring safety and longevity. For commercial projects, geotechnical soil testing minimizes risks of structural failure by addressing potential issues like settlement or soil instability.
Through various testing methods and detailed reports, engineers gain invaluable insights into subsurface conditions, enabling precise planning and execution. This page will discuss the methods, benefits, and significance of geotechnical soil testing, helping you make informed decisions for your next project.
Secure Your Commercial Project with Reliable Soil Insights—Contact Us Today!
Ensures Foundation Stability
Identifies soil's load-bearing capacity to design safe foundations.
Minimizes Delays
Addresses soil issues early to avoid costly construction setbacks.
Prevents Structural Failures
Detects risks like settlement and instability before construction begins.
Supports Code Compliance
Ensures adherence to local safety and building regulations.
Enhances Design Accuracy
Provides precise data for tailored foundation and site preparation plans.
Benefits of
Geotechnical Engineering Soil Testing?
As previously stated, geotechnical engineering soil testing is a critical step in ensuring the safety, stability, and success of construction projects. By analyzing soil properties and subsurface conditions, this process helps identify potential risks and provides data-driven solutions. Whether you’re planning a residential build, commercial development, or infrastructure project, soil testing lays the foundation for informed decisions and long-term stability.
In short, geotechnical engineering soil testing prevents costly issues like foundation cracking, slope failures, or structural instability. By providing detailed reports, they empower engineers to design safer, more efficient foundations.
Don’t Leave Your Project’s Success to Chance. Get Expert Soil Testing Now!
The Importance of Soil Testing and Geotechnical Reports
Soil testing and geotechnical reports are indispensable for commercial developments, mapping out potential issues before they arise. These reports compile detailed findings from soil investigations to guide design decisions for foundations, retaining walls, and drainage systems.
Key Elements of a Geotechnical Report:
- Site Investigation Results: Details of subsurface conditions, including soil composition and stability.
- Design Recommendations: Suggestions tailored to soil properties and project needs.
- Risk Assessments: Identifies potential hazards like soil erosion or water table fluctuations.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensures alignment with local building codes and standards.
By addressing these elements, geotechnical reports provide the blueprint for safe and efficient construction. Thorough documentation not only mitigates risks but also saves time and money by reducing the likelihood of project delays and structural issues. For peace of mind on your next commercial project, call on Piers and Piles for expert soil testing and geotechnical reporting and ensure that your project is built to last!
How to Get a Geotechnical Soil Test in Long Island, Brooklyn, or Queens
When it comes to ensuring the safety and stability of your construction project, precision matters. At Piers and Piles, we offer comprehensive geotechnical soil testing tailored for Long Island, Brooklyn, and Queens. With state-of-the-art equipment and a team dedicated to delivering accurate data, we’re here to support your project from start to finish.
Why Choose Piers and Piles?
- Advanced Equipment: We utilize cutting-edge tools to provide detailed insights into soil conditions.
- Comprehensive Testing Services: From seismic testing to load testing and beyond, we cover every critical aspect of soil evaluation.
- Experienced Professionals: Our team is committed to accuracy, ensuring your project meets safety standards and building codes.
- 30-Year Warranties: We stand behind our work with industry-leading warranties, ensuring our peace of mind for the long-term.
Call Us Today to Schedule an Assessment!
An Overview of Geotechnical Soil Tests
Geotechnical soil testing is a set of tests that identify subsurface conditions, ensuring the stability of construction projects. These tests provide critical insights into soil properties, helping engineers design safe and durable foundations. By identifying potential risks like uneven settlement or soil instability, geotechnical testing minimizes project delays and structural failures. Whether for roadways, buildings, or large-scale infrastructure, comprehensive soil evaluations are vital for meeting local regulations and industry standards. Investing in accurate lab and field tests ensures your construction project begins with a solid foundation.
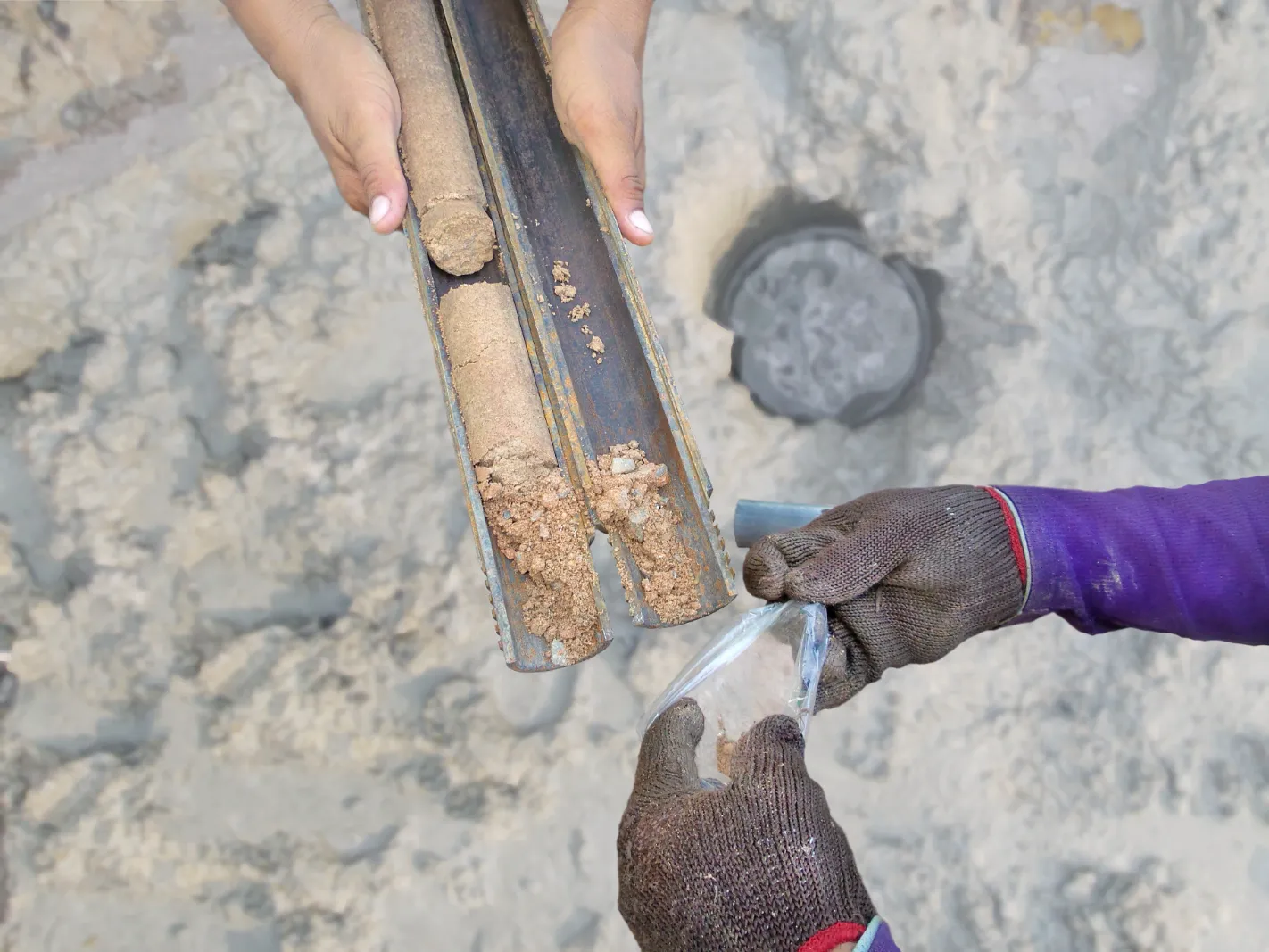

Common Types of Geotechnical Soil Tests
In a geotechnical soil test, subsurface conditions help engineers evaluate critical soil properties such as load-bearing capacity, compaction, moisture content, and permeability. By using methods like the Standard Penetration Test (SPT), Percolation Test, and Atterberg Limits Test, engineers can design foundations and drainage systems that meet local regulations and are build as solid as possible.
Below, we’ve outlined some of the main types of geotechnical soil tests. Click on an of the test names to find out more about that test type.
Permeability Test
The Permeability Test evaluates a soil’s ability to transmit water, essential for groundwater management and drainage solutions. By measuring flow rates, the Permeability Test helps engineers design effective dewatering and waterproofing systems. This ensures projects meet performance and safety standards.
Consolidation Test
The Consolidation Test measures soil settlement under applied loads over time, providing essential data for foundation design. Engineers use Consolidation Test results to predict long-term soil behavior, minimizing structural settlement risks. This test is crucial for ensuring durable and stable structures.
Proctor Test
The Proctor Test evaluates the optimal moisture content and maximum dry density required for soil compaction. By compacting soil in layers and measuring density, this test ensures structural stability and strength. The Proctor Test is a cornerstone in geotechnical engineering for achieving reliable compaction results.
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) measures soil resistance to penetration by driving a sampler into the ground. It provides critical data on soil density, strength, and stratification, making it an essential method for foundation and geotechnical engineering.
By using the Standard Penetration Test, engineers can determine whether soil conditions are suitable for safe and stable construction projects.
Environmental Tests
Environmental tests assess potential environmental hazards and risks associated with a construction site. These tests evaluate air, water, and soil quality to identify pollutants or contaminants that could impact the environment or human health.
Environmental tests ensure compliance with environmental regulations, mitigate risks, and support sustainable development. Key aspects include testing for hazardous materials, groundwater contamination, and ecological impacts, enabling safe and environmentally responsible construction practices.
Seismic Tests
Seismic tests evaluate soil stability and behavior during earthquakes or seismic events. These tests analyze subsurface conditions to determine the soil’s capacity to withstand ground motion and vibrations.
By identifying liquefaction risks, fault lines, and other seismic vulnerabilities, engineers can design earthquake-resistant structures. Seismic testing ensures compliance with safety codes and enhances the resilience of buildings in earthquake-prone areas like Long Island.
Soil Contamination Tests:
A soil contamination test identifies harmful substances such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, pesticides, and other pollutants in the soil. It ensures the site is safe for construction and meets environmental regulations. Contaminated soil can lead to health risks, structural issues, and regulatory non-compliance. Testing provides data to guide remediation efforts, ensuring a clean and secure foundation for construction projects.
By using the Standard Penetration Test, engineers can determine whether soil conditions are suitable for safe and stable construction projects.
Soil Bearing Capacity Test
The Soil Bearing Capacity Test determines the maximum load a soil can safely support without risking failure or excessive settlement. This test involves applying incremental loads to soil samples or in-situ testing with tools like plate load tests.
The results help engineers design foundations that distribute loads effectively and ensure long-term stability for structures. The Soil Bearing Capacity Test is essential for evaluating the soil’s strength and ensuring safety in construction projects.
Percolation Test
The Percolation Test evaluates the soil’s ability to absorb and drain water by measuring water seepage rates. This test is essential for designing septic systems, leach fields, and stormwater management solutions.
By using the Percolation Test, engineers ensure proper drainage and compliance with local regulations, preventing waterlogging and system failures.
Moisture Content Analysis
Moisture Content Analysis measures the water levels in soil to assess compaction, stability, and suitability for construction. Accurate Moisture Content Analysis ensures optimal conditions for foundation and structural support. This test helps prevent settlement or instability caused by excessive or insufficient moisture.
Shear Strength Test
The Shear Strength Test measures soil resistance to sliding forces, crucial for assessing stability in slopes and foundations. By determining shear strength, engineers can predict soil performance under stress. The Shear Strength Test is essential for ensuring slope safety and structural integrity.
Specific Gravity Test
The Specific Gravity Test determines the density of soil particles relative to water, aiding in engineering calculations. This test is essential for analyzing soil composition and its suitability for construction. The Specific Gravity Test supports accurate design and material selection in geotechnical projects.
Atterberg Limits Test
The Atterberg Limits Test assesses soil plasticity by measuring liquid and plastic limits under varying moisture conditions. This test classifies soil behavior, especially in clay and silt, helping engineers predict structural changes.
With the Atterberg Limits Test, projects achieve accurate soil categorization, ensuring optimal design and stability.
California Bearing Ratio (CBR)
The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test evaluates the load-bearing capacity of subgrade soil for roadways and pavements. It compares soil resistance to penetration with a standard material, ensuring infrastructure can handle traffic loads. The California Bearing Ratio test is vital for durable and safe transportation projects.
Step-by-Step Guide to Geotechnical Engineering Soil Testing
A soil contamination test identifies harmful substances such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, pesticides, and other pollutants in the soil. It ensures the site is safe for construction and meets environmental regulations. Contaminated soil can lead to health risks, structural issues, and regulatory non-compliance. Testing provides data to guide remediation efforts, ensuring a clean and secure foundation for construction projects.
Engineers extract core samples from multiple depths across the site to assess soil composition, moisture levels, and structural properties. These samples undergo laboratory testing using advanced equipment to measure factors like compaction, shear strength, and bearing capacity. This step uncovers potential risks, such as subsurface variability or inadequate load-bearing capabilities, that could affect the construction process.
Once the lab results are finalized, engineers analyze the data to identify trends and potential challenges. Using these insights, they provide tailored recommendations for foundation designs, drainage systems, and soil improvement techniques. This process ensures that the project accounts for unique site conditions, reducing risks and enhancing structural stability.
The process concludes with the delivery of a detailed geotechnical report that includes all testing results, analyses, and actionable recommendations. This report acts as a guide for construction teams, ensuring that every decision—from foundation design to site preparation—is informed by precise, reliable data. It also helps streamline the construction process by addressing potential issues upfront.
Work with experienced cootractors to ensure every step of your geotechnical soil testing is thorough, accurate, and aligned with your project’s needs.
Common Challenges in Geotechnical Tests on Soils and How to Overcome Them
Performing geotechnical tests on soils can be complex, but knowing the common hurdles helps streamline the process. Here are typical challenges and solutions to ensure accurate and actionable results.
Challenges and Solutions:’
- Variable Soil Types: Unpredictable subsurface conditions require diverse testing methods.
Solution: Use multiple testing techniques like SPT and Atterberg Limits. - High Water Tables: Excessive moisture can skew test results.
Solution: Employ moisture barriers or dewatering techniques before testing. - Limited Site Access: Tight spaces or remote locations make equipment setup difficult.
Solution: Use portable, advanced equipment designed for restricted access.
The Value of Expertise:
By engaging experienced geotechnical engineers, these challenges can be mitigated. Professional oversight ensures data accuracy and reduces risks during construction.
Streamline Your Soil Testing—Partner with Experts Today!
Interpreting Geotechnical Soil Tests for Commercial Success
Interpreting data from geotechnical soil tests is critical for making informed decisions in commercial construction. Test results provide actionable insights that guide foundation design and other structural considerations.
Key Data Points from Soil Tests:
- Load Capacity: Determines the soil’s ability to support structural loads.
- Moisture Content: Indicates potential water-related risks like erosion or swelling.
- Shear Strength: Reveals the soil’s resistance to sliding forces.
- Plasticity Index: Predicts behavior under varying environmental conditions.
How Test Results Inform Construction:
- Modify foundation type for soil stability.
- Design drainage systems to manage water-related risks.
- Reinforce areas prone to settlement or slope instability.
Real-world applications of accurate soil testing reduce long-term costs and improve safety.
Geotechnical Engineering Soil Testing: Final Thoughts
Geotechnical engineering soil testing is your roadmap to safer, more efficient commercial builds. With tailored strategies and advanced tools, this process ensures stable foundations and long-lasting structures. Investing in professional soil testing minimizes risks, adheres to regulations, and avoids costly project delays. From detailed reports to actionable recommendations, geotechnical engineering lays the groundwork for success.
Don’t Leave Your Project’s Foundation to Chance—Get Expert Soil Testing Now!
Click here to check out our FAQ page for commonly asked questions about soil testing, or reach out to us to speak with an expert.